|
This article is slightly outdated as of 0.6.0 for both Scrap Mechanic and the modding tool. This page is waiting for an update due to 0.6.0 release.
The mod tool eases the process of creating and sharing mods. With the mod tool you can easily manage all your mods through the Steam Workshop. If you make and upload changes to your mods, they will be automatically updated for your mod's subscribers. At its current state the mod tool supports blocks and parts creation, terrain assets and custom games.
Before you create your mod, please read through our guidelines. If these guidelines are not followed we might have to ban your mod from the workshop.[ | ]
Opening the mod tool[ | ]
1. Go to your Steam Library
2. Open the drop-down above the search field on the left and select "Tools"
3. Enter "Scrap Mechanic Mod Tool" into the search (you can also copy it from here)
4. Click "Start"
How to Make a Basic Building Block Mod[ | ]
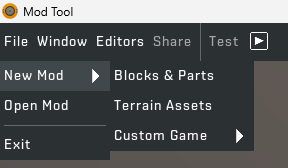
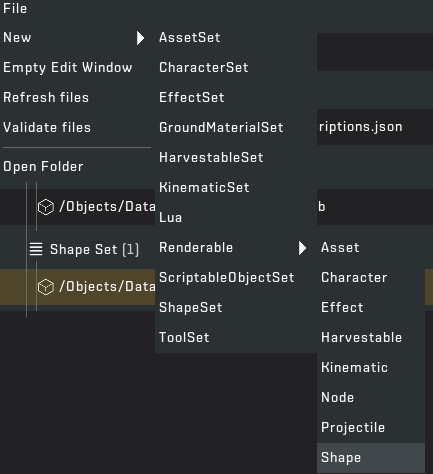
STEP 1: Launch the "Scrap Mechanic Mod Tool". Then press "File" > "New Mod" > "Blocks & Parts" which creates a new Blocks and Parts mod.
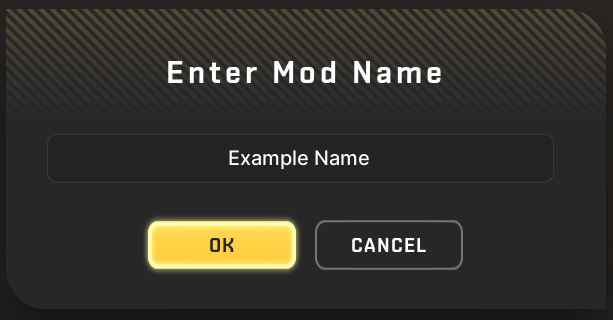
STEP 2: Type in a name for your mod and press "Ok".
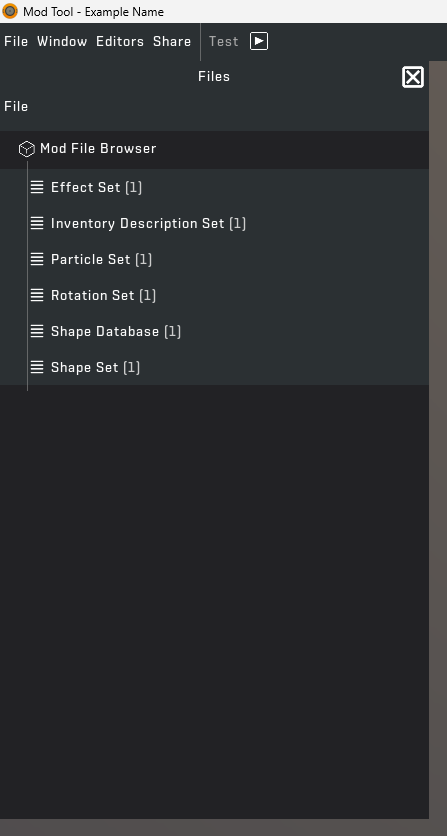
STEP 3: After pressing "Ok" your screen should look like this.
This is how you will be able to manage what is in your mod. Double clicking on the tabs will expand them, showing the files related to the category under them. If they aren't needed, you can also delete the following files by right clicking on each item: /Effect/Database/EffectSets/example.json, /Particles/particles.json, /Objects/Database/rotationsets.rotationset.
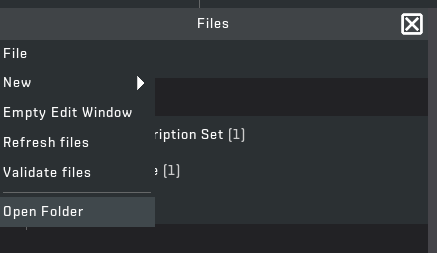
STEP 4: Open the folder by clicking "File" > "Open Folder" make sure to click "File" in the file explorer window.
STEP 5: Now let's put the textures we want for our new block mod in the Textures folder Located here: Objects > Textures
We're going to use these 512x512 texture files.
Texture resolution is affected by tiling value, it is recommend to use 512x512 resolution for tiling of 4, 1024x1024 resolution for tiling of 8 and etc.
For more in-depth information about textures in Scrap Mechanic see How to Make Textures for Scrap Mechanic
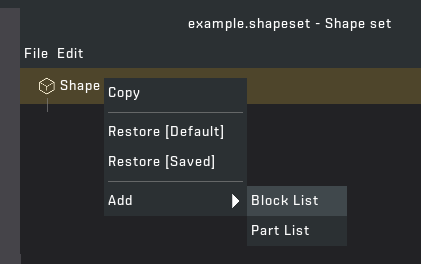
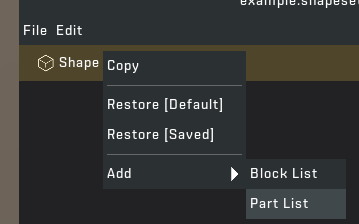
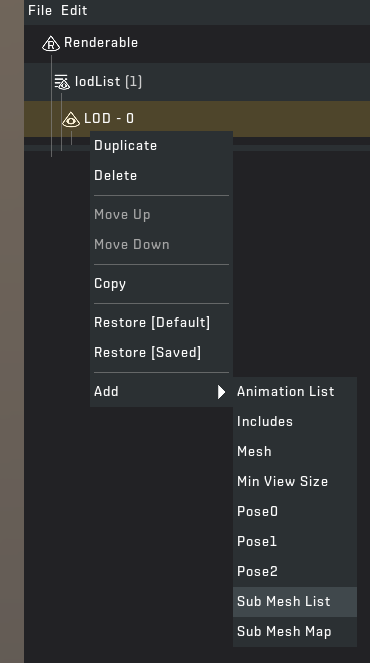
STEP 6: Re-open the mod tool and click on /Objects/Database/ShapeSets/example.shapeset (you can rename this by right clicking) to open the file in the mod tool. Create a new "Shape" by right clicking on Shape Set and go to "Add" > "Block List".
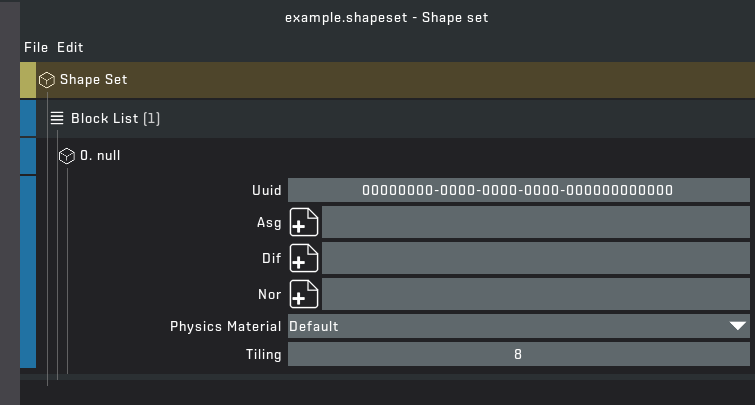
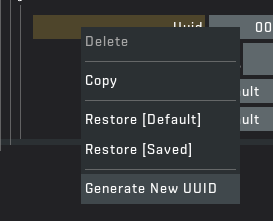
You may be confused so let me go through some things. The yellow text means the "File" has been changed since last save. If you want to save click "File" > "Save". In the list, each block contains data that can be easily edited. Each block requires a UUID which helps the game link everything together. If you right click on the UUID field you can generate a new UUID. Asg, Dif and Nor is a path to each texture file relative to the game files or mod files. The physics material tells the game what material the block should be: Cardboard, Fruit, Foliage, etc. Tiling is how many blocks you place down before the texture repeats.
STEP 7: Fill out the block data as you want. Input textures by right clicking on the "File" button which opens your file explorer. You can add additional data by right clicking on 0. null/uuid and adding any data you would like. Once you are done make sure you save the file.
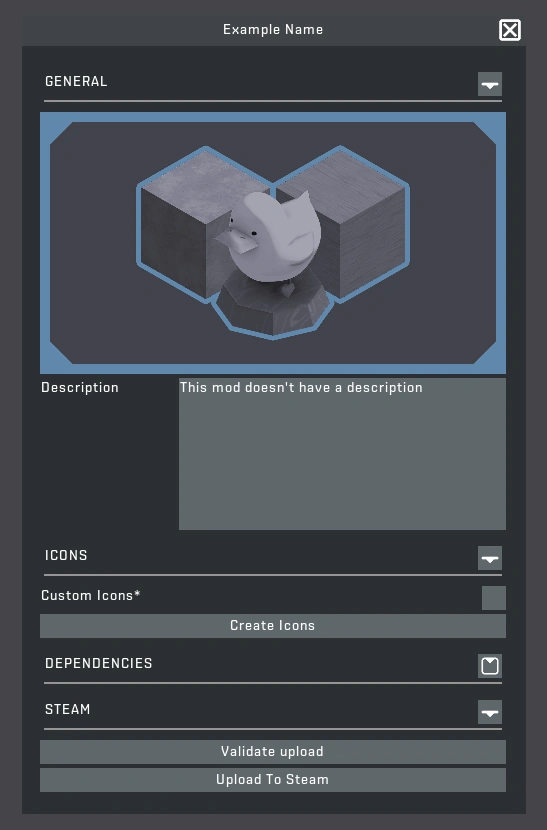
STEP 8: Generating icons or editing the mod description can be done by clicking on "Share" at the top. You can edit the mod description to your liking. Press "Create Icons" to allow the mod tool to compile all assets and create an Icon Map. You can add dependencies here and upload the mod to Steam.
STEP 9: Congratulations! You've made your very first block mod.
If everything worked, you should now be able to find your new block in the inventory.
Here's how the new block looks in-game. If you're pleased with how your block looks you can share your mod on the Steam Workshop by pressing the "Upload To Steam" button in the Scrap Mechanic Mod Tool. If you want other people in the community to be able to find it, you also have to change the visibility from hidden to public.
How to Make a Basic Part Mod[ | ]
STEP 1: First off, you need to make a model. Before exporting, make sure your model is placed at the origin with the pivot centered. Also the the pivot axis of the model should follow the example below.
| Axis | Direction |
| X | Right |
| Y | Up |
| Z | Depth |
In Maya we use cm (centimeters) as our working unit, so the scale of our models and the Maya grid matches the grid in-game. The engine supports various file formats but we recommend .fbx or .obj when exporting. We also recommend that while you model, you think about how your part will fit in the in-game grid.
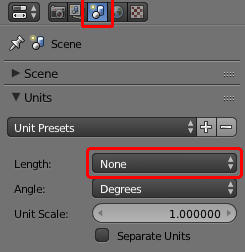
In Blender you can use use either "Metric" or "None" for your units. If you use metric, then one meter = one block. If you use "none", then one "unit" = one block. The unit setting is in the Properties window under the Scene tab.
STEP 2: Now let's put the textures for our new part mod in the Textures folder Located here: Objects > Textures
We're going to use these 256x256 texture files.
For more in-depth information about textures in Scrap Mechanic see "How to Make Textures for Scrap Mechanic" further down.
STEP 3: Open the mod tool and navigate to the shapeset you created last time. Next create a new part list.
STEP 4: Create a new part by right clicking on the part list and press New > [Default]. Generate a new UUID as shown below.
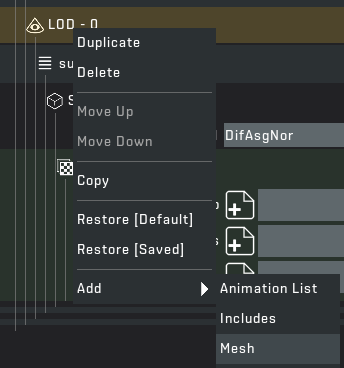
STEP 5: Create a new renderable. This is the data for how a mesh should be rendered in game. This contains models for different LODs and textures.
STEP 6: Now it's time to add the proper information to your renderable. Create a new sub mesh list as seen below. Then fill out the data related to the DIF, ASG & NOR file locations. Make sure to put the mesh in as well.
If you want to use other shaders, eg. glass, leaves (renders both sides, transparency), liquid, or even skeleton animation, you can select which shader you'd like to use by clicking on the shader dropwdown menu automatically selected on DifAsgNor, for ones which don't need a normal map, they will use a flat one, meaning they won't have depth, but they will have correct shading.
STEP 7: Go back to your part in the shape set and add the new renderable we just created. MAKE SURE TO SAVE!
How to Make Textures for Scrap Mechanic[ | ]
Scrap Mechanic materials can make use of three different textures: diffuse, ASG and normal maps. Diffuse defines the base color and texture for your material. ASG allows you to make areas transparent, specular, glowing or reflective. Normal maps are used for faking the lighting of bumps and dents.
Diffuse[ | ]
It's important to remember that if you want to be able to use the in-game Paint Tool on your block, you will need to make use of the alpha channel in the diffuse. The darker an area of the alpha is, the more it will be affected by the coloring.
ASG[ | ]
Then we make what we call an ASG texture (Alpha, Spec, Glow… And Reflectivity). We use values of various color channels to affect the material.
| Channel | Function | Value results |
| Red channel (Alpha) | Determines the transparency of the texture. | No red value = added transparency. |
| Green channel (Spec) | Sets the specular level of the texture. | No green value = no spec. |
| Blue channel (Glow) | Makes the texture emissive and glowing. | No blue value = no glow. |
| Alpha channel (Reflectivity) | Adds reflection to the texture. | White alpha value = maximum reflection. |
–What does "no value" mean?
–I'll start in order. When editing the all channels, I recommend that you use 2 colors-black and white (+ all shades of gray). The darker the color, the smaller the value and vice versa.
-The easiest way to make ASG textures is to make different maps corresponding to each channel, the amount of maps you'll need depends on the part you are making. The minimum you'll need is 2, Specular and Reflectivity maps.
-Alpha map of ASG texture is also only supported by few materials, most important one including "alpha" at the end of the material name.
Normal Maps[ | ]
Finally we make a normal map. These can be generated or created using various tools such as Quixel Ndo, Maya, Zbrush and many more.
For the speed of creating a normal map, I recommend the website "SmartNormap 2.0" (http://www.smart-page.net/smartnormal/)
How do I make a normal map? We export the "DIF" texture, for example, to png. After this action, we upload the image to the site listed above and then download it.
Most modelling programs also allow you to "bake" geometry of one model onto another model as normal map.
Exporting textures[ | ]
Make sure that you save your textures as .tga files and use the 32bits/pixel resolution to include the alpha channel. For normal maps, make sure the file name ends with "_nor.tga".
Block Properties[ | ]
Adding blocks to Scrap Mechanic is quite simple, since you don't need to assign any meshes. But there are various properties you can use depending on what type of block you'd like to make. Below are various properties that define the behavior of your block.
UUID[ | ]
An UUID uniquely identifies your block or part. You can easily generate one through the mod tool. If you want to replace an old part instead of adding one, you need to reuse your old UUID for the new part.
| Example UUID |
| e2543ac2-ed58-46d0-a593-13ff8d11e02b |
Texture Paths[ | ]
Mod texture paths
| Texture definition | File path | Result |
| "dif" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_dif.tga" | Links to your diffuse texture in your mod library. |
| "asg" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_asg.tga" | Links to your ASG texture in your mod library. |
| "nor" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_nor.tga" | Links to your normal map texture in your mod library. |
Changing "$CONTENT_DATA" to "$GAME_DATA"/"$SURVIVAL_DATA" allows you to link to an already existing texture from the game's own assets.
Material[ | ]
The material property defines what kinds of textures are used.
| Material definition | Result |
| "Dif" | Only diffuse is used for this material. |
| "DifAsg" | Diffuse and ASG are used for this material. |
| "DifAsgNor" | Diffuse, ASG and normal maps are used for this material. |
| "DifAsgNorAlpha" | Same as "DifAsgNor", though red value in ASG texture is used to create transparency. |
| "Glass" | Diffuse, ASG and normal maps are used for this material. Makes block transparent. |
| "DifAsgNorFlip" | Renders both sides of all faces of the mesh. Can be useful if you're making a window. |
| "UVAnimDifAsgNor" | Renders a UV positions sequence, requires "custom" next to it |
More materials can be found in the drop-down list.
Color[ | ]
This sets the default color for the material in-game. This will change when you paint the object with the Paint Tool.
| Example hex code | Result |
| "0000ff" | Makes blue the default color |
Ratings[ | ]
Ratings decide the stats of your block, each stat such as, weight (mass), durability, friction, buoyancy and flammability define the material of your block.
| Rating type | Value | Result |
| Weight | 1-10 | Very light or heavy mass |
| Durability | 1-10 | Fragile or durable
(Max is indestructible) |
| Friction | 1-10 | Slippery or frictionfull on ground |
| Buoyancy | 1-10 | Sinks or floats in water
(Affected by weight) |
| Flammable | Yes/No | Whether the block is flammable or not
(Affected by durability) |
Tiling[ | ]
Depending on your texture size, you should match a tiling value.
| Tiling value | Texture resolution | Result |
| 1 | 128 x 128 texture | Tiles every block |
| 2 | 256 x 256 texture | Tiles every 2nd block |
| 4 | 512 x 512 texture | Tiles every 4th block |
| 8 | 1024 x 1024 texture | Tiles every 8th block |
| 16 | 2048 x 2048 textures | Tiles every 16th block |
Physics Material[ | ]
Physics materials affects the sound and particles of an object.
| Cardboard |
| Default |
| Dirt |
| Fabric |
| Fence |
| Foilage |
| Fruit |
| Glass |
| Graval |
| Mechanical |
| Metal |
| Plastic |
| Potato |
| Rock |
| Sand |
| Sledgehammer |
| Tape |
| Water |
| Wood |
Glass Key[ | ]
Renders the block material as transparent, adjust Specular and Reflection properties and ASG to imitate glass.
Part Properties[ | ]
Parts can have more advanced behavior than blocks (e.g. Shapes, Scripts). Below are various properties that define the behavior of your part.
UUID[ | ]
UUID is your unique id for the part/block. You can easily generate one at by right clicking on the UUID title. If you want to replace an old part instead of adding one, you use the same UUID as the one you wish to replace.
| Example UUID |
| e2543ac2-ed58-46d0-a593-13ff8d11e02b |
Renderable[ | ]
"renderable" defines what mesh will be rendered plus the submeshes, textures and their material. Most meshes consists of just one mesh, but adding a submesh allows another part of the mesh to use a different set of textures and material.
Mod texture list paths[ | ]
Choose which textures to refer to by writing in the correct folder path.
| Texture definition | File path | Result |
| "dif" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_dif.tga" | Links to your diffuse texture in your mod library. |
| "asg" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_asg.tga" | Links to your asg texture in your mod library. |
| "nor" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Textures/examplename_nor.tga" | Links to your normal map texture in your mod library. |
Changing "$CONTENT_DATA" to "$GAME_DATA"/"$SURVIVAL_DATA" allows you to link to an already existing texture from the game's own assets.
Mesh path[ | ]
Choose which mesh to refer to by writing in the correct folder path.
| Mesh definition | File path | Result |
| "mesh" | "$CONTENT_DATA/Objects/Mesh/examplename.fbx | Links to your mesh in your mod library |
Changing "$CONTENT_DATA" to "$GAME_DATA"/"$SURVIVAL_DATA" allows you to link to an already existing mesh from the game's own assets.
Material[ | ]
The material property defines what kinds of textures are used.
| Material definition | Result |
| "Dif" | Only diffuse is used for this material. |
| "DifAsg" | Diffuse and asg are used for this material. |
| "DifNor" | Diffuse and normal maps are used for this material. |
| "DifAsgNor" | Diffuse, asg and normal maps are used for this material. |
| "DifAsgNorAlpha" | Same as "DifAsgNor", though red value in asg texture is used to create transparency. |
| "Glass" | Diffuse, asg and normal maps are used for this material. Makes block transparent. |
| "DifAsgNorFlip" | renders both sides of all faces of the mesh. Can be useful when your making a window. |
| "UVAnimDifAsgNor" | Renders a UV positions sequence, requires "custom" next to it |
More materials can be found in the drop down list.
Color[ | ]
This sets the default color for the material in-game. This will change when you paint the object with the Paint Tool.
| Example hex code | Result |
| "0000ff" | Makes blue the default color |
Collision[ | ]
There are 3 different colliders: box, cylinder and hull.
Box[ | ]
The box collision will create a box surrounding your mesh.
| Example box values | Result |
| "box": { "x": 1, "y": 2, "z": 3 } | Creates a box collision with the dimensions corresponding to the values of x, y, z. |
Cylinder[ | ]
A cylinder collision is good to use for wheels or round objects.
| Example cylinder values | Result |
| "cylinder": { "diameter": 7, "depth": 1, "margin": 0.5, "axis": "Z" } | Diameter is the size of the cylinder. Depth sets the thickness. Margin sets the bevel amount, pretty much rounds the edges. Axis determines in which direction the cylinder is facing. |
Hull[ | ]

A hull collision is a collision mesh in which you can apply to your part by adding it to the part in the parts list by right clicking on it, once you have the hull added you can add a "col" which defines it's collision mesh, it must use the format ".obj" in order for it to work correctly, once you have assigned the mesh, the 3 coordinates which are in the base hull represent the size of the box in which you can weld, or use to place the part down/placing on it.
The hull collision also supports the sticky, and rotation set modifiers.
Hull [Old/Pre-Survival][ | ]
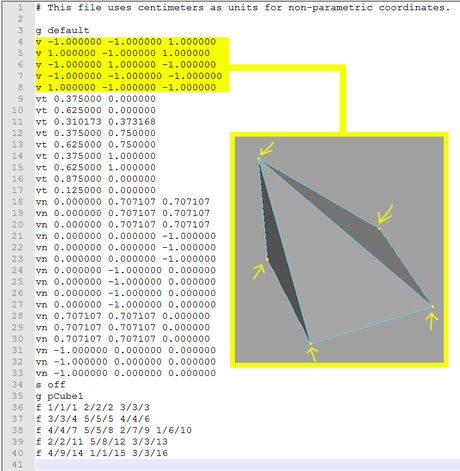
A hull collision is created using a pointlist. It draws lines between vertex coordinates. These vertex coordinates can be found, if for example you open a .obj file with a text editor. However it's good to make a simplified mesh to not get too many coordinates in the list.
| Example hull values | Result |
| "hull": {
"x": 1, "y": 1, "z": 1, "pointList": [ { "x": 1.0, "y": -1.0, "z": -1.0 }, { "x": -1.0, "y": -1.0, "z": -1.0 }, { "x": -1.0, "y": -1.0, "z": 1.0 }, { "x": 1.0, "y": -1.0, "z": 1.0 } ] } |
x, y, and z defines the size of a space/cube which the pointlist will fit itself in
Each row in the pointList of x, y, z refers to the location of a single vertex point. Together the rows create the hitbox. |
Ratings[ | ]
Ratings decide the stats of your block, each stat such as, weight (mass), durability, friction, buoyancy and flammability define the material of your block.
| Rating type | Value | Result |
| Weight | 1-10 | Very light or heavy mass |
| Durability | 1-10 | Fragile or durable
(Max is indestructible) |
| Friction | 1-10 | Slippery or frictionfull on ground |
| Buoyancy | 1-10 | Sinks or floats in water
(Affected by weight) |
| Flammable | Yes/No | Whether the block is flammable or not
(Affected by durability) |
Physics Material[ | ]
The physics material affects the sound and particles when an object is hit. (for example by a Sledgehammer or a Spud Gun projectile)
| Cardboard |
| Default |
| Dirt |
| Fabric |
| Fence |
| Foilage |
| Fruit |
| Glass |
| Graval |
| Mechanical |
| Metal |
| Plastic |
| Potato |
| Rock |
| Sand |
| Sledgehammer |
| Tape |
| Water |
| Wood |
Interactive Part List Functions (OUTDATED)[ | ]
Interactive functions[ | ]
Interactive parts include buttons and switches, engines, seats and everything that has a specific function. Here's all the functions you can add to your part list:
| "bearing": { } | bearing |
| "timedjoint": { } | controller |
| "lever": { } | switch |
| "button": { } | button |
| "sensor": { } | sensor |
| "radio": { } | radio |
| "horn": { } | horn |
| "logic": { } | logic gate |
| "timer": { } | timer |
These are easy to implement, just add them to your part list and you're done. If you wish to make them animate, you'll need some additional lines and models.
Pose animation[ | ]
Lets take a closer look on the part list for an ordinary button:
Here you can see that it's not much different from the other part lists. The material has been changed to support pose animations.
Pose animations are simple, and don't require any animation.
You simply export two models, one with the model in its off state, in this case an un-pressed button. And one in its on state, pushed button.
It's important that these two models are identical, and that you only move vertices to get the other state.
Advanced interactive functions[ | ]
These require some more lines to work properly, we recommend copying the .json file from the game files and then edit them to fit your mod. You can find the .json for all interactive parts here:
Steam\steamapps\common\Scrap Mechanic\Data\Objects\Database\ShapeSets
| "spring": { } | suspension |
| "steering": { } | driver seat |
| "seat": { } | seat |
| "engine": { } | engine |
| "thruster": { } | thruster |
| "tone": { } | tote bot head |
| "spotlight": { } | headlamp |
Inventory Descriptions[ | ]
Blocks/parts will not have a name or description until you add them in an inventoryDescriptions.json file.
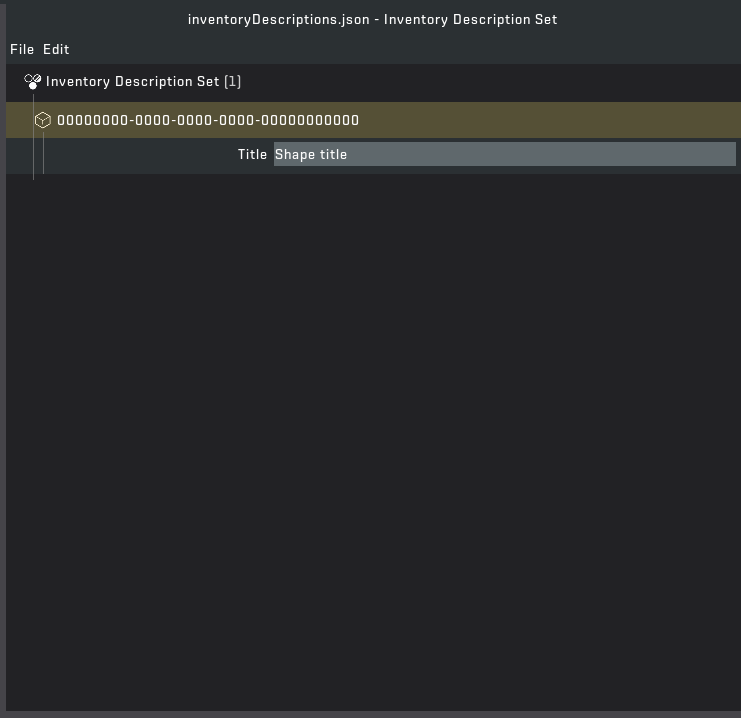
STEP 1: Open the following file in the Mod Tool "/Gui/Language/English/inventoryDescriptions.json"
STEP 2: Rename the first entry with the block/part uuid.
STEP 3: Add the title of the block/part.
STEP 4: You can add a description and keywords by right clicking on the UUID field.
STEP 5: Save the file and test it in game. The inventory will now display the name and description that you selected.
Crafting[ | ]
- Warning: Custom crafting recipes are currently not supported in workshop-compatible mods
Crafting is important for any block or item that you want to be accessible in Survival Mode, though it is relatively simple.
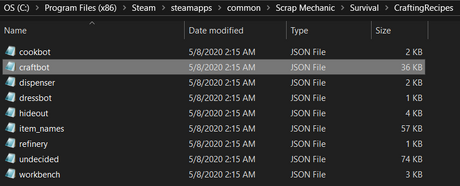
Recipes under their corresponding bench name will be crafted at that bench, with "hideout" being the trader, "dispenser" the Mechanic Station where the Cookbot is built and "workbench" the default Craftbot that will spawn in certain structures.

This is the vanilla code for the "Concrete1" crafting recipe as an example.
The first itemId is that of the block you want to craft, followed by how many of this item you want to be crafted under quantity, and how long (in seconds) it takes to craft this item under craftTime.
The quantity under ingredientList states how many of that specific block or part is necessary, i.e., four water for ten concrete.
Crafting (Custom Game)[ | ]
Crafting in custom games is similar to the previously mentioned guide and is relatively simple.
If you copied the base survival game, you should be able to add and edit the .json files like usual for survival mods, though you will have to specify where the files are in the "Crafter.lua" file which you can find in the survival interactables scripts folder.
Icons[ | ]
Many people are inattentive, which is why they spend a lot of time on icons...
Icons are made easily and quickly!
- Launch the mod tool program
- Select the desired mod
- Click "Share" > "Create Icons"
(if the object is invisible, it's icon must be created manually)
Tools[ | ]
Creating a Tool Set[ | ]
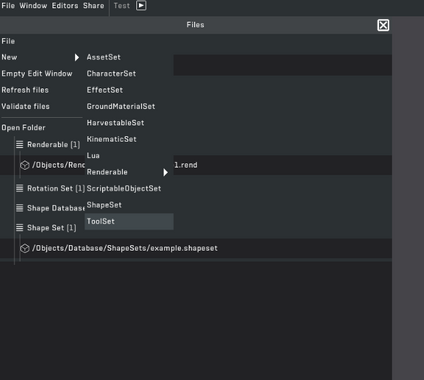
A tool is one of those things you see ingame that you can hold and interact with (eg. the sledgehammer), to create a tool, first you'll have to go into the mod tool and in the mod file browser click "file > new > toolset".
Once you have done that, rightclick on the new toolset and select "Open External" and open it with notepad or a similar text editing program.
Then type the following: "{"toolList":[]}", and save, once you've done that, you may now restart the mod tool and open the toolset.
Adding to Tool Database[ | ]
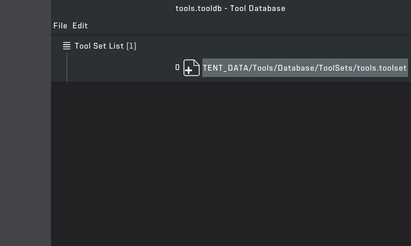
For your tool to work, you'll have to create a new tools database.
Open your mod folder and find the tools directory, and in that folder, create a new text file with the extension ".tooldb", once you've done that, you can reload the mod tool and open the new tool database.
To add a toolset, select "tool set list > new > [default]", then add the file as you would for most other selection slots in the mod tool.
Adding tools[ | ]
Now that you have a toolset, and a tooldatabase, we can actually start making some tools.
To create a tool, select the tools list in the tool set and click "new > [default]".
In the new tool, you can add a debug name, a preview renderable, or a new uuid, by clicking on the new tool, you can add a preview rotation, this will correct the original rotation, or you can add your own rotation if you wish, the preview shouldn't use bones, and should have the same coordinates system as the parts models, though the sizing of the whole model doesn't matter too much unless you want it as a part as well.
Other Tutorials[ | ]
These tutorials should help you with some topics that are not yet covered or not covered deeply on this wiki.
GUI[ | ]
Third-Party Utilities and Websites[ | ]
These third-party utilities and websites are used for modding Scrap Mechanic, but are not officially supported by Axolot Games.
Texturing[ | ]
Utilities that aid in the creation of textures for Scrap Mechanic.
- SM ASG Compiler (combines multiple textures into one ASG texture)
Crafting Recipe Editors[ | ]
Utilities for changing crafting recipes in Survival Mode.
- SMEMT (currently only supports Craftbot recipes)
Websites[ | ]
- Improved SM Lua API Reference (better version of the official SM API Reference)
- MyGUI Layout Converter (converts widget position and size data to percentages for compatibility with all display resolutions)